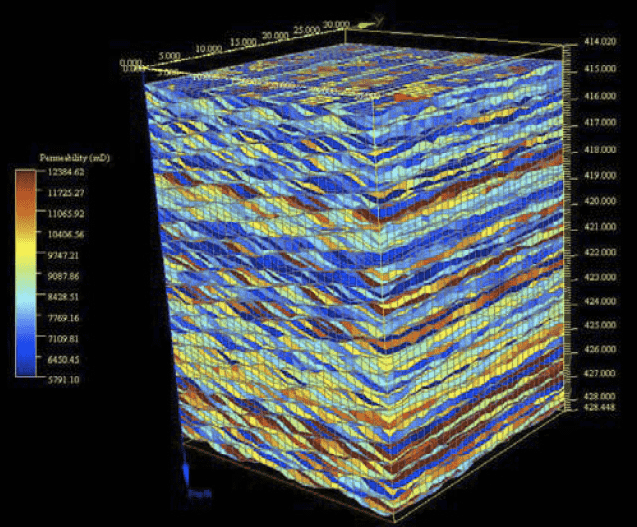
Geoscientists have often been frustrated by the arbitrary assignment of petrophysical log cut-offs to define reservoir intervals capable of hosting producible hydrocarbon. The traditional practice is to derive "pseudo-permeability" from well logs such as gamma ray, density, and sonic. However, this indirect approach can introduce large errors in estimates of...
Enhancing Reservoir Visualization with Spectral Decomposition
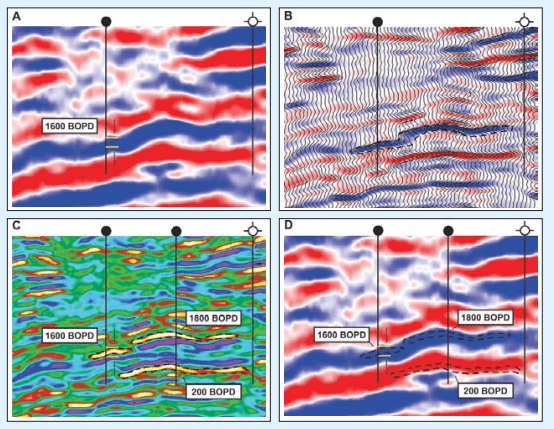
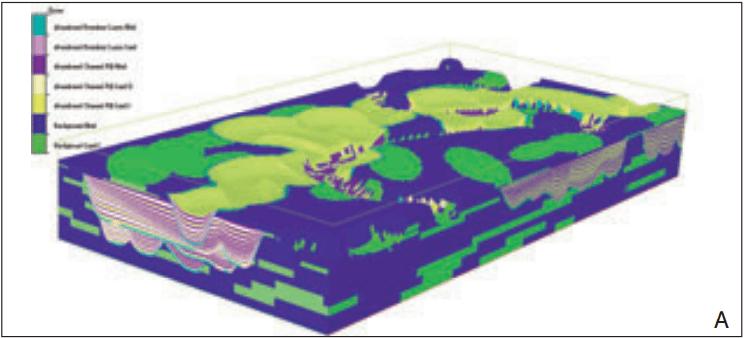
Spectral decomposition adds value to visualization and interpretation workflows by revealing details normally overlooked in full bandwidth seismic displays. In Alberta's Blackfoot field, the oil- and gas-producing Lower Cretaceous Glauconite Member contains shales and quartz sands of lacustrian and channel origin. The hydrocarbon reservoirs typically occur where the porous sands...
Implicit net-to-gross in the petrophysical characterization of thin-layered reservoirs
A new workflow has been devised to characterize the petrophysical properties of two, thin-layered, heterolithic log facies from a turbidite reservoir. The methodology is based on a published modelling technique that enables an extremely accurate reconstruction of the fine-scale lithological and sedimentological reservoir heterogeneities and a thorough integration of petrophysical...
Seeing between a rock and a hard place
Braided fluvial reservoirs can host significant volumes of hydro-carbons, being high net/gross ratio, and are often considered to be relatively easy to characterize. But this is not always the case, as confirmed in a recent study conducted by Houston-based reservoir services company Geotrace Technologies Inc. The Misoa Sandstone reservoir in...
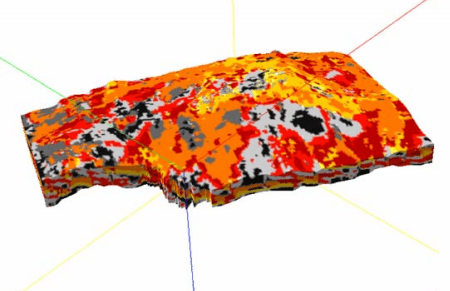
3D geologic modelling of channelized reservoirs: applications in seismic attribute facies classification
Geological models are usually used qualitatively in seismic interpretation. This paper illustrates that quantitative representations of detailed geological models can significantly enhance seismic attribute interpretation through facies classification. When applying seismic attribute classification to reservoir facies mapping, one often faces such typical questions as: Which attributes should be used as...
Introducing geological processes in reservoir models
Reservoir modeling and reservoir simulation are based on data collected at multiple scales with resolution ranging from sub-millimeter to tens of meters. New software using knowledge of the geological processes forming the reservoir rock now makes it possible to generate more accurate reservoir models, thereby improving prediction of both production...
Small-scale reservoir modeling tool optimizes recovery offshore Norway
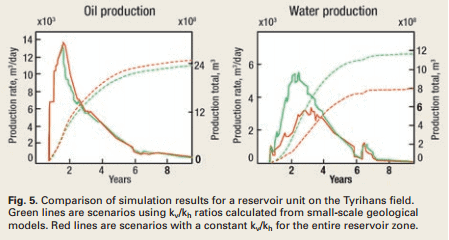
Modeling of small-scale bedding geometries improves recovery estimates in Norwegian oil fields, yielding added value of at least 16 million barrels. Demands for improved oil recovery prompted the Norwegian oil company, Statoil, to evaluate geologically complex oil and gas-condensate fields offshore Norway with a new approach. Here, major sections of...
Vertical Seismic Facies Detection Through Unsupervised 3D Voxel Based Seismic Facies Classification Applied to a Turbidite Field in Campos Basin, Brazil
Nowadays, automatic seismic facies analysis techniques have been growing as an important interpretation tool for the oil exploration industry. Depending on the reservoir knowledge, the seismic facies analysis could be supervised by a priori geological information, or could be unsupervised, when there are not enough data to guide the analysis....
Reservoir challenges of heterolithic tidal sandstone reservoirs in the Halten Terrace, mid-Norway
Production from the Halten Terrace hydrocarbon province (Mid-Norwegian shelf) is mainly from heterolithic siliciclastic successions as well as diagenetically altered sandstones. Eight hydrocarbon fields are currently in production, which produce c. 840 000 BBL oil equivalent per day, with several new fields expected to come on stream in the next decade. This...
Permeability Rescaling And Near-Wellbore Modeling Of Heterogeneities In Lower Jurassic Tidal-Influenced Tilje Formation, Heidrun Field
The Lower Jurassic Tilje Formation constitutes an important reservoir in the Heidrun Field. Reservoir characterization of its strongly tide-influenced deposits is challenging due to the high degree of heterogeneity. This is especially true for the estimation of permeability data from different scales (core plug measurements, log data and well test...