CALGARY, Alberta - Visitors to the Geomodeling Booth (#2306) at the 2013 SEG Annual Meeting will see six demonstrations of breakthrough software applications and services for seismic attribute analysis and reservoir characterization for both conventional and unconventional environments: Advanced Techniques for Unconventional Seismic and Microseismic Interpretation in AttributeStudio Using Stratal...
Improving Reservoir Characterization and Simulation With Near-Wellbore Modeling
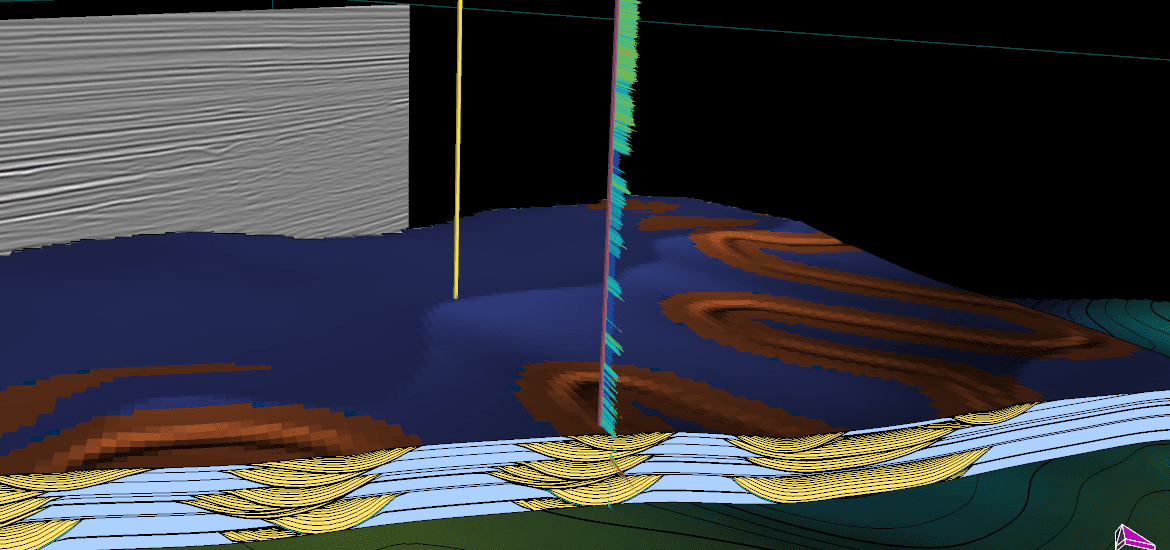
New reservoir characterization methods are needed to integrate multiscale exploration and development data, particularly at the interface between well and field models. In this paper, we illustrate a novel workflow involving high-resolution near-wellbore modeling (NWM), which allows us to accurately include seismic, wireline data, image logs, and well core logs...
Geomodeling to Showcase AVAZ Visualization for Fractured Reservoir Analysis at SEG 2012 in Las Vegas
CALGARY, Alberta — Geomodeling Technology Corp., a leading provider of innovative software for the upstream oil and gas industry, will be demonstrating AVAZ Vector Visualization for fractured reservoir characterization at the upcoming SEG Annual Meeting and Exhibition, November 4-9 in Las Vegas, Nevada. AttributeStudio’s Vector Visualization for directional attributes highlights...
AVAZ Vector Visualization
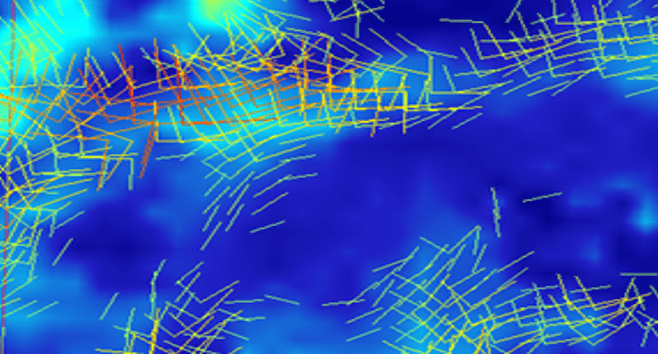
AttributeStudio™ from Geomodeling includes breakthrough features for fractured reservoir characterization using visualization and analysis of AVAZ, VVAZ, and other directional attributes. Anisotropic gradients and velocity differences captured by directional seismic attributes such as AVAZ and VVAZ can be correlated to fracture density and orientation in unconventional reservoirs. AttributeStudio’s Vector Visualization...
Geomodeling Releases AttributeStudio™ 7.3
AVAZ Vector Visualization for Unconventional Plays CALGARY, Alberta--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Geomodeling Technology Corp., a leading provider of seismic analysis and cross-scale modeling software for the upstream oil and gas industry, today announced release of AttributeStudio™ 7.3, its state-of-the-art seismic attribute interpretation software. AttributeStudio 7.3 includes breakthrough features for fractured reservoir characterization using...
AttributeStudio Unconventional
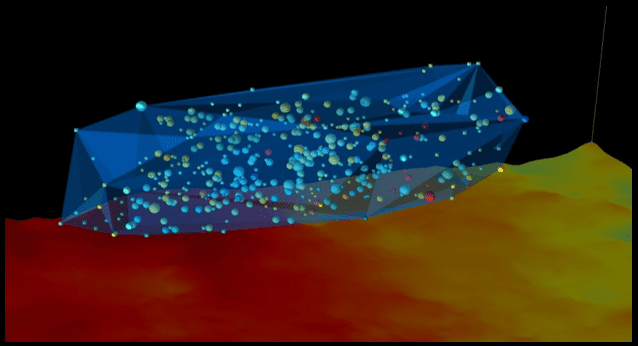
AttributeStudio Unconventional from Geomodeling is a comprehensive suite of advanced tools for reservoir characterization of unconventional, fractured shale and carbonate plays. AttributeStudio Unconventional enables you to correlate seismic, microseismic, well log, and engineering data from hydraulic fractures into an integrated interpretation of fractured formations. MICROSEISMIC DATA INTERPRETATION Using AttributeStudio Unconventional,...
Geomodeling to Showcase Advanced Quantitative and Unconventional Intrepretation at GeoConvention 2012 in Calgary
New releases of AttributeStudio, SBED, and ReservoirStudio will be demonstrated CALGARY, Alberta -- Geomodeling Technology Corp., a leading provider of innovative software for the upstream oil and gas industry, will be demonstrating new releases of AttributeStudio, SBED, and ReservoirStudio focused on quantative and unconventional interpreation at the CSPG/CSEG/CWLS GeoConvention 2012...
Geomodeling Releases AttributeStudio™ 7.2
Advanced Features for Quantitative and Unconventional Seismic Interpretation CALGARY, Alberta--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Geomodeling Technology Corp., a leading provider of seismic analysis and cross-scale modeling software for the upstream oil and gas industry, today announced release of AttributeStudio™ 7.2, its state-of-the-art seismic attribute interpretation software. AttributeStudio 7.2 includes neural network analysis for advanced...
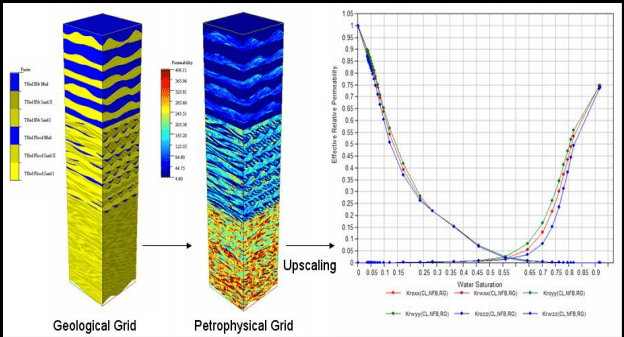
Estimation of Reservoir Heterogeneity from the Depositional Environment in Reservoir Characterization of a CHOPS Field
The major challenge in reservoir characterization is to estimate the effective porosity and the permeability of the reservoir due to reservoir heterogeneity. Often the vertical and the horizontal permeability are not considered separately in 3D geo-cellular models and in the reservoir simulations. Conventional reservoir modeling extrapolates all of the small-scale data to full-field scale...
SBED Biogenic Structure Modeling
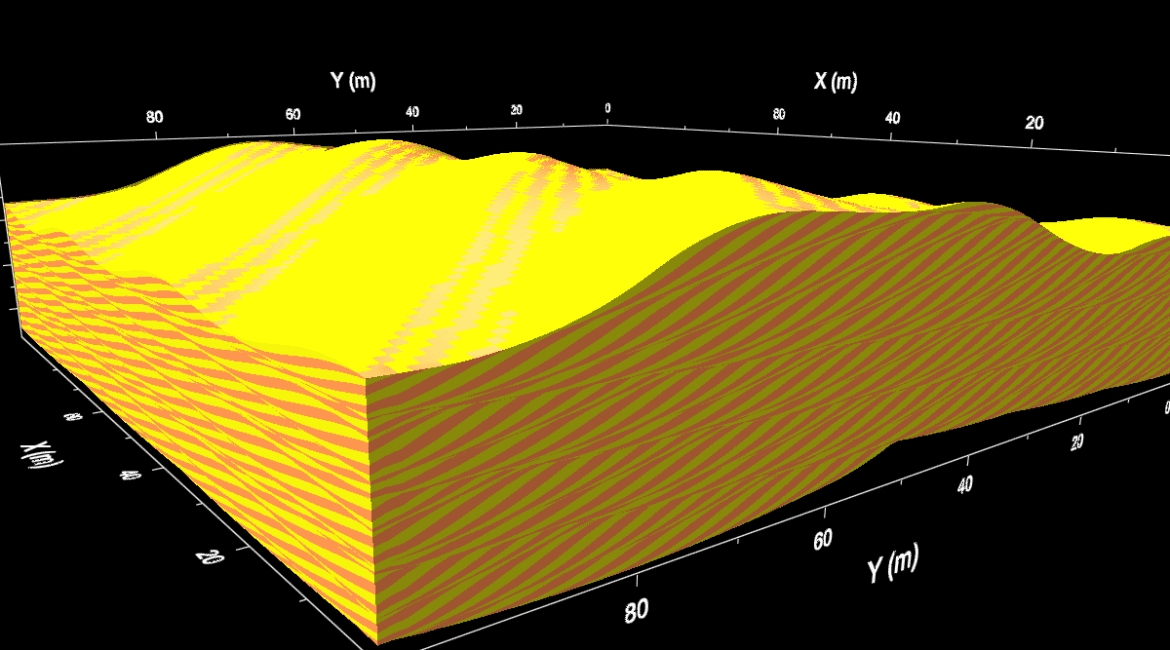
SBED™ Biogenic Structure Modeling accurately simulates the activities of burrowing organisms on reservoir facies at the lamina scale and estimates their effects on petrophysical properties using flow-based upscaling. Bioturbation within a substrate can add to sedimentary heterogeneity and alter horizontal and vertical permeability. Understanding the subtle changes in permeability that...